Machine Learning 101 - Understanding the Core Concepts before diving into
ML - classic definitions
Machine learning is the science (and art) of programming computers so they can learn from data.
General Definition:
“Machine learning is the field of study that gives computers the ability to learn without being explicitly programmed.”
— Arthur Samuel, 1959
Engineering-Oriented Definition:
“A computer program is said to learn from experience E with respect to some task T and some performance measure P, if its performance on T, as measured by P, improves with experience E.”
— Tom Mitchell, 1997
What ML is?
If i could summarize the whole of ML in one sentence it could be….
“A collection of tools and techniques that transforms data into meaningful decisions by making classifications on whether someone will like this film or quantitative predictions like how tall someone is.”
So when we use ML techniques to classify something we call it classification and when we make prediction on something we call it prediction.
When we talk about classification, we’re asking, “What category does this data belong to?” like for example Will this person like this movie? Is this email spam or not? It’s about putting things into distinct buckets.
While on the other hand, prediction is a bit more like forecasting the future. It’s about taking some data and estimating something continuous. How much will this stock price rise next month? Predictions involve estimating values rather than sorting things into categories.
These two approaches—classification and prediction—are the foundation of most ML tasks.
Then what is AI, ML, DL, Gen AI?
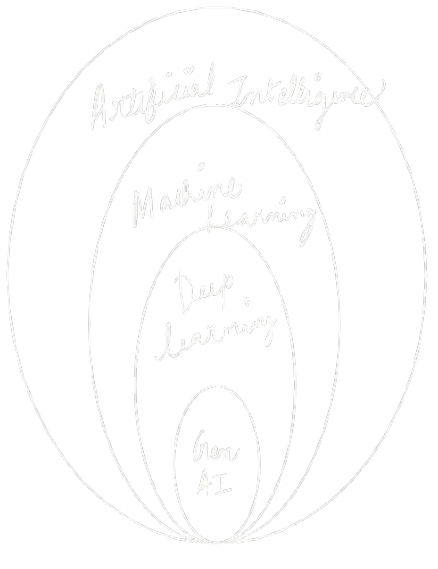
AI, Machine Learning (ML), Deep Learning (DL), and Generative AI (Gen AI) are all quite interrelated concepts.
-
So from the above image, AI (Artificial Intelligence) is the broadest concept, which refers to any technique or system that mimics human-like intelligence, reasoning, and problem-solving.
-
ML (Machine Learning) is a subset of AI that focuses on algorithms that allow machines to learn patterns from data and make decisions based on that information, without being explicitly programmed. ML systems “learn” from past experiences (data) to make predictions or decisions.
-
DL (Deep Learning) is a specialized subfield within ML that uses artificial neural networks with many layers (hence “deep”) to model complex patterns. It excels at tasks like image recognition, nlp, and speech recognition, due to its ability to process vast amounts of unstructured data.
-
Gen AI (Generative AI) refers to AI systems that are designed to generate new content like text, images, music, or code, based on learned patterns. It typically involves deep learning models (particularly neural networks) to create novel outputs that resemble the data the system was trained on. Examples include GPT (for text generation), DALL·E (for image generation), and Stable Diffusion.
I will write more in-depth blogs on them in the upcoming days which will provide greater clarity.